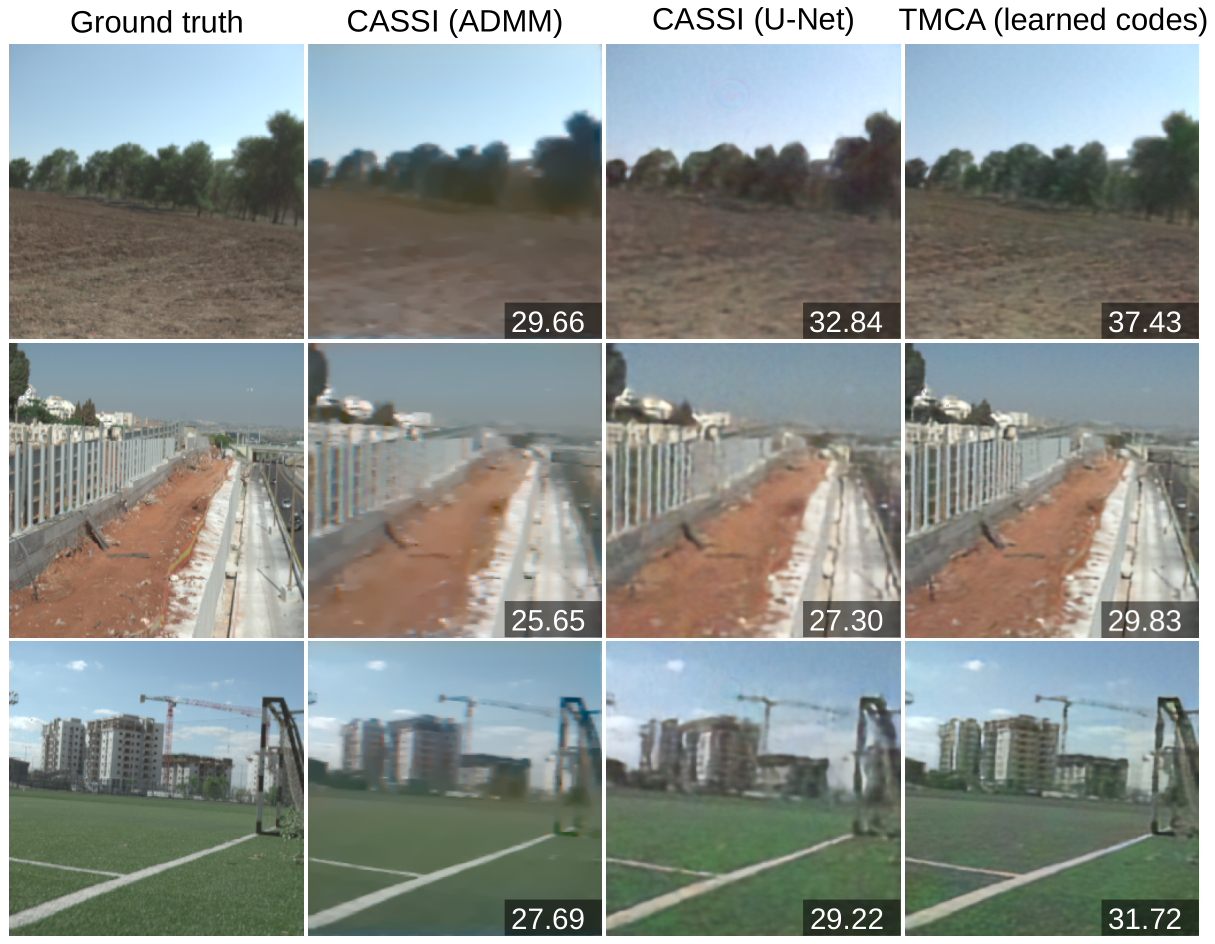
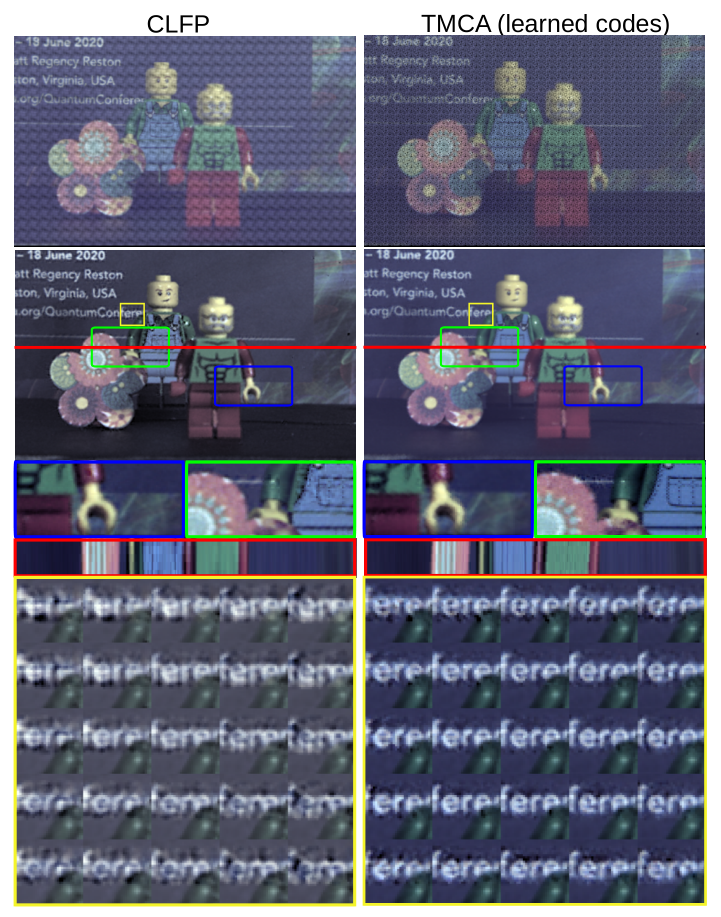
ABSTRACT
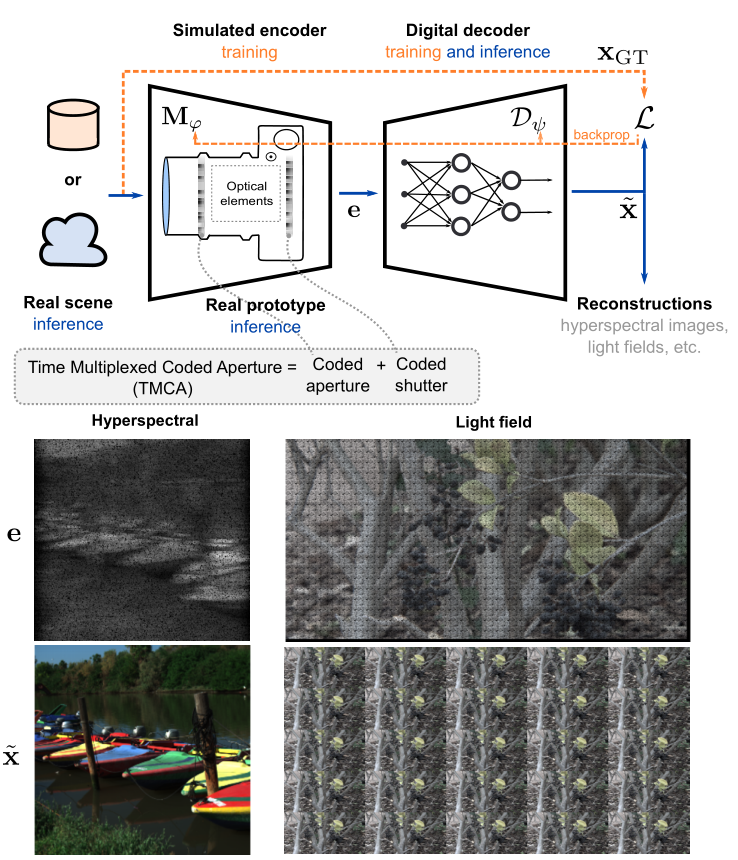
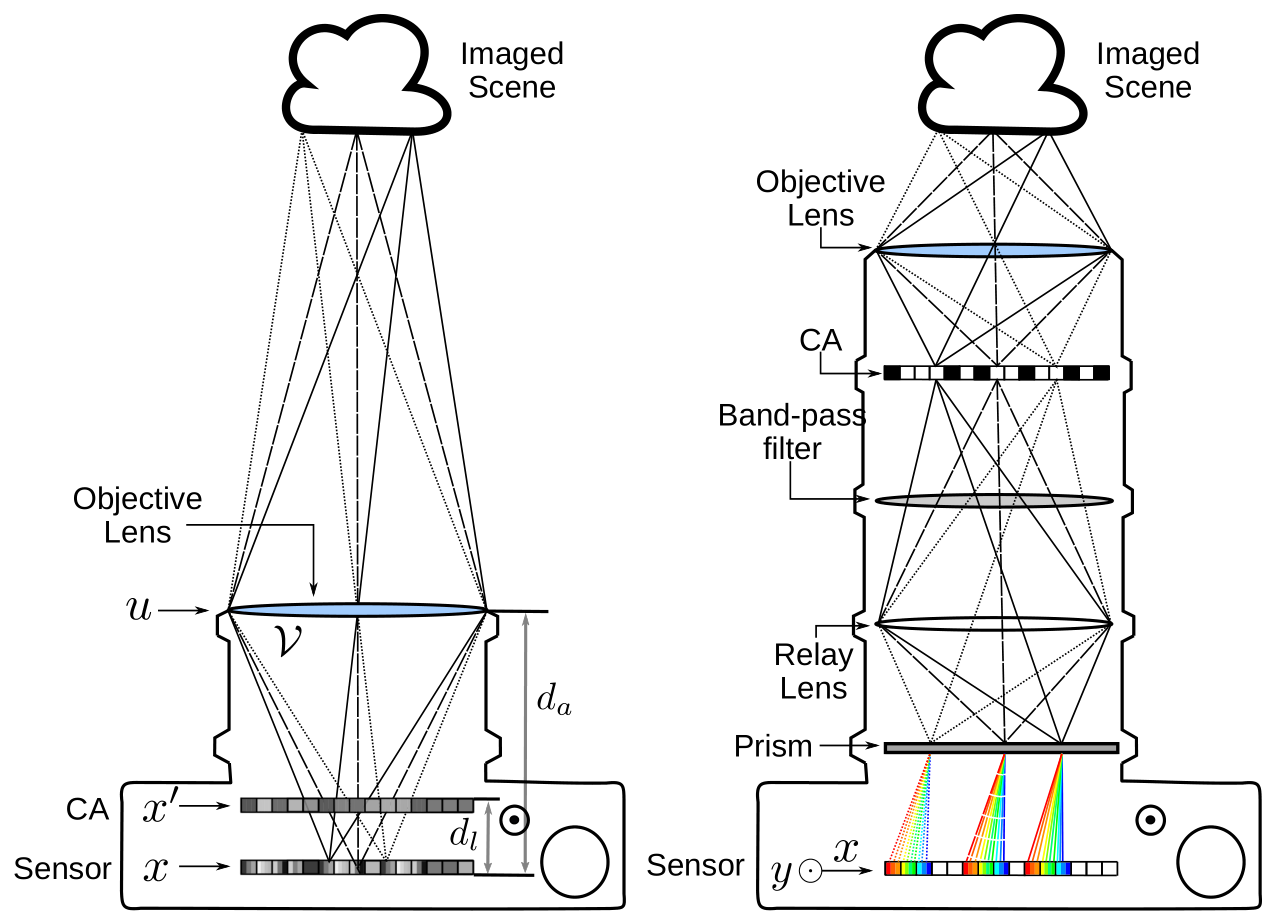
Compressive imaging using coded apertures (CA) is a powerful technique that can be used to recover depth, light fields, hyperspectral images and other quantities from a single snapshot. The performance of compressive imaging systems based on CAs mostly depends on two factors: the properties of the mask’s attenuation pattern, that we refer to as “codification”, and the computational techniques used to recover the quantity of interest from the coded snapshot. In this work, we introduce the idea of using time-varying CAs synchronized with spatially varying pixel shutters. We divide the exposure of a sensor into sub-exposures at the beginning of which the CA mask changes and at which the sensor’s pixels are simultaneously and individually switched “on” or “off”. This is a practically appealing codification as it does not introduce additional optical components other than the already present CA but uses a change in the pixel shutter that can be easily realized electronically. We show that our proposed time-multiplexed coded aperture (TMCA) can be optimized end to end and induces better coded snapshots enabling superior reconstructions in two different applications: compressive light field imaging and hyperspectral imaging. We demonstrate both in simulation and with real captures (taken with prototypes we built) that this codification outperforms the state-of-the-art compressive imaging systems by a large margin in those applications.